+351916395152
Understanding Artrose
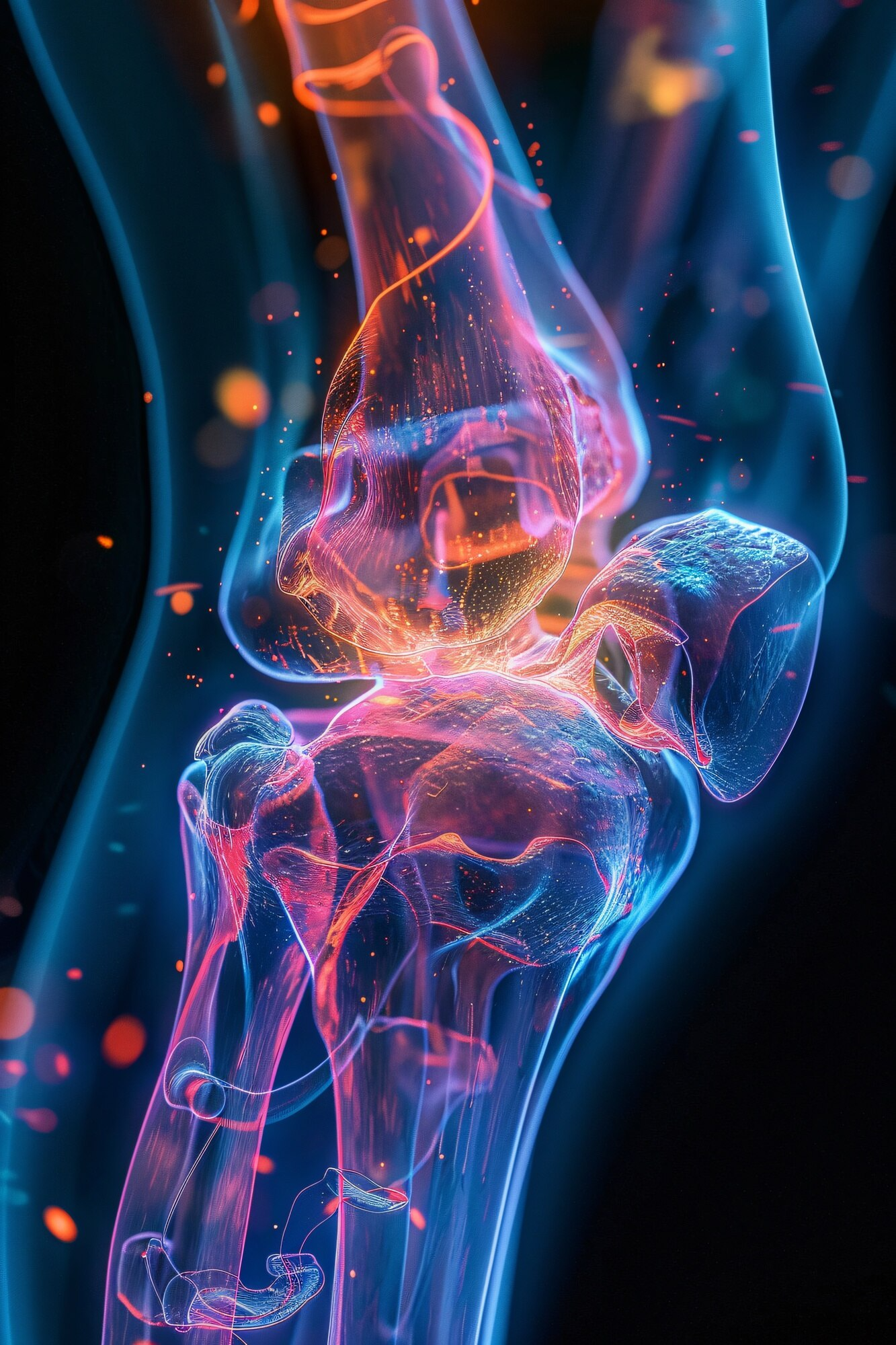
Artrose, also known as osteoarthritis, is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone. It typically affects the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
Causes and Risk Factors of Artrose
Common Causes
Artrose can be caused by aging, joint injury, obesity, and genetic factors. Additionally, occupations that involve repetitive stress on certain joints may increase the risk.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for artrose include family history, gender (more common in women), bone deformities, and certain metabolic disorders.
Reducing Risk
Maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, and avoiding joint injuries can help reduce the risk of developing artrose.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Artrose
01
Early Symptoms
Common early signs of artrose include joint pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. These symptoms may worsen over time.
02
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, imaging tests like X-rays and MRIs, and in some cases, joint fluid analysis.
03
Progression Evaluation
Assessing the level of joint damage and evaluating the impact on daily activities is crucial to determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Medical Treatments for Artrose
Medication
Commonly prescribed medications for artrose include pain relievers, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
Injections
Injections of hyaluronic acid or corticosteroids directly into the affected joint can provide relief from pain and improve joint function.
Surgery
For severe cases, surgical options like joint repair, joint replacement, or realignment procedures may be considered to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Lifestyle Modifications for Managing Artrose
Dietary Adjustments
Include anti-inflammatory foods like berries, green leafy vegetables, and fatty fish in your diet to help reduce artrose-related inflammation.
Joint Protection
Avoid activities that put excessive stress on the joints and use assistive devices or ergonomic tools to minimize joint strain.
Stress Management
Practicing relaxation techniques, such as yoga and meditation, can help reduce stress and ease artrose-related discomfort.
Exercises and Physical Therapy for Artrose
Range of Motion Exercises
These exercises aim to maintain or improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness, promoting better joint function and mobility.
Strength Training
Building muscle strength around the affected joints can help support and stabilize the joints, reducing pain and preventing further damage.
Physical Therapy
A customized physical therapy program can improve joint range of motion, reduce pain, and enhance overall physical function in artrose patients.
Tips for Reducing Pain at Home Due to Artrose
01
Posture
Practice good posture to reduce strain on your joints, especially the spine, hips, and knees.
02
Rest
Balance activity with rest, and avoid staying in the same position for too long to alleviate joint discomfort.
03
Supportive Footwear
Wear supportive, cushioned footwear to minimize impact and reduce stress on weight-bearing joints.
04
Environment Modifications
Make adjustments at home, such as using handrails and grab bars, to improve safety and reduce the risk of falls.

Experience a different treatment, focused on your needs and with results at Awaking Connections by Patricia Cassique.




